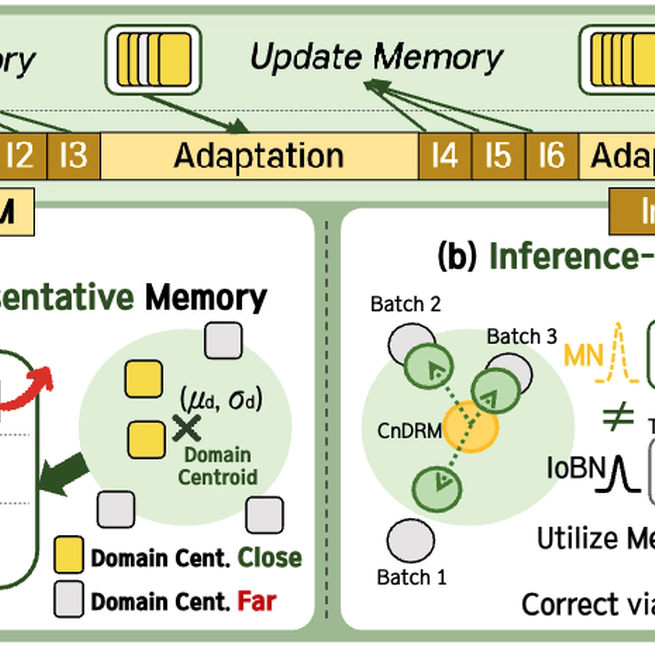
Test-Time Adaptation (TTA) adjusts models using unlabeled test data to handle dynamic distribution shifts. However, existing methods rely on frequent adaptation and high computational cost, making them unsuitable for resource-constrained edge environments. To address this, we propose SNAP, a sparse TTA framework that reduces adaptation frequency and data usage while preserving accuracy. SNAP maintains competitive accuracy even when adapting based on only 1% of the incoming data stream, demonstrating its robustness under infrequent updates. Our method introduces two key components. (i) Class and Domain Representative Memory (CnDRM), which identifies and stores a small set of samples that are representative of both class and domain characteristics to support efficient adaptation with limited data; and (ii) Inference-only Batch-aware Memory Normalization (IoBMN), which dynamically adjusts normalization statistics at inference time by leveraging these representative samples, enabling efficient alignment to shifting target domains. Integrated with five state-of-the-art TTA algorithms, SNAP reduces latency by up to 93.12%, while keeping the accuracy drop below 3.3%, even across adaptation rates ranging from 1% to 50%. This demonstrates its strong potential for practical use on edge devices serving latency-sensitive applications. The source code is available at https://github.com/chahh9808/SNAP.
May 1, 2025
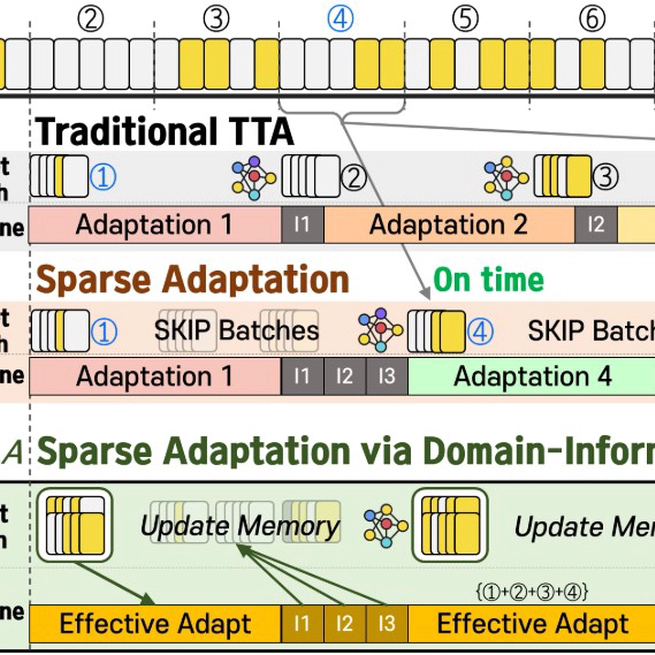
We propose TESLA Time-Efficient Sparse and Lightweight Adaptation strategy for real-time mobile applications, which skips adaptation for specific batches to increase the inference sample rate. Our method balances model accuracy and inference speed by accumulating domain-informative samples from non-adapted batches and sparsely adapting them.
Jun 3, 2024
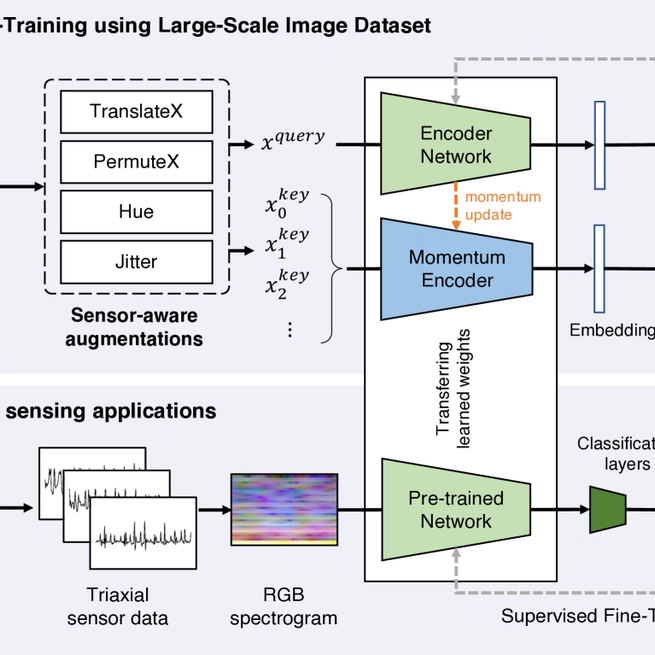
Pre-training representations acquired via self-supervised learning could achieve high accuracy on even tasks with small training data. Unlike in vision and natural language processing domains, pre-training for IMU-based applications is challenging, as there are few public datasets with sufficient size and diversity to learn generalizable representations. To overcome this problem, we propose IMG2IMU that adapts pre-trained representation from large-scale images to diverse IMU sensing tasks. We convert the sensor data into visually interpretable spectrograms for the model to utilize the knowledge gained from vision. We further present a sensor-aware pre-training method for images that enables models to acquire particularly impactful knowledge for IMU sensing applications. This involves using contrastive learning on our augmentation set customized for the properties of sensor data. Our evaluation with four different IMU sensing tasks shows that IMG2IMU outperforms the baselines pre-trained on sensor data by an average of 9.6%p F1-score, illustrating that vision knowledge can be usefully incorporated into IMU sensing applications where only limited training data is available.
Feb 29, 2024
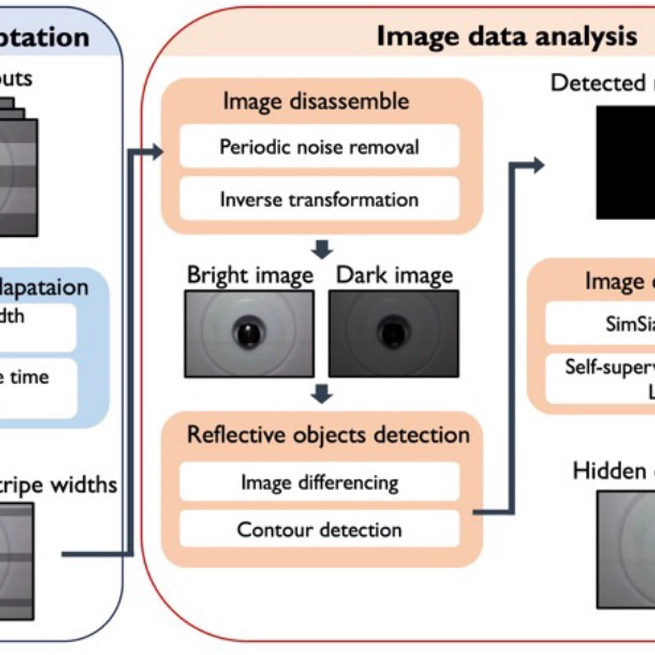
With the rapid advancements in surveillance camera technology, there has been a surge in crimes involving illegal filming using hidden cameras. However, current solutions necessitate slow manual scanning processes that require thousands ofworkers within a city to ensure coverage. To address this challenge, we introduce Sherlock, a fully automated hidden camera detection system that utilizes a drone in combination with a flickering flashlight. To expedite the scanning process and accommodate the irregular movements of the drone, Sherlock leverages the rolling shutter effect to capture images when the flashlight is turned on and off within a single frame. This methodology enables Sherlock to efficiently identify reflective objects and detect hidden camera lenses among them. To demonstrate the feasibility of Sherlock, we present a proof-of-concept evaluation by deploying a drone in various environments to detect and locate hidden cameras.
Oct 25, 2023